Toothache and Dental Abscess
Toothache
Toothache is one of the most common reasons why people see an Emergency Dentist. Toothache can present as a constant or intermittent sharp, stabbing, dull or throbbing pain.
Dental Abscess
A dental abscess is a collection of pus that can form inside the teeth, in the gums, or in the bone that holds the teeth in place. It is caused by a bacterial infection. Dental abscess is one of the most common reasons why people see an Emergency Dentist.

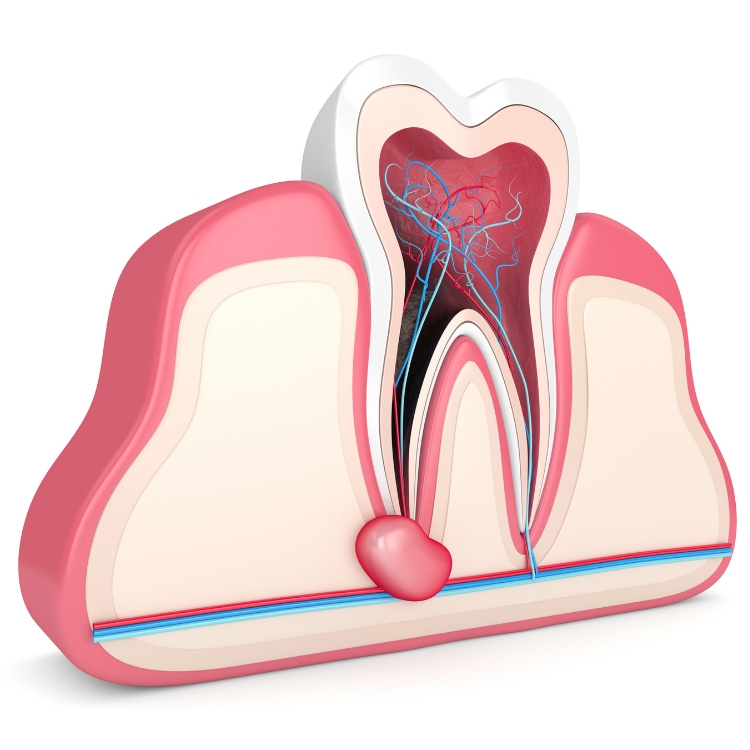
Types of dental abscesses
There are two types of abscesses
- Periapical Abscess: An abscess at the end of a tooth is called a periapical abscess.
- Periodontal Abscess: An abscess in the gum is called a periodontal abscess.
What are the common causes of dental pain?
Toothache can be caused by;
- Tooth decay (Caries)
- Dental abscess
- Cracked tooth or broken tooth
- Broken filling
- Issues with braces
- Gum disease (Periodontal disease)
- Jaw pain (Jaw joint pain called TMJ pain)


How long should you wait to see a dentist for a toothache?
You should see your regular dentist or Emergency Dentist if the toothache
- Last more than 2 days
- Pain on biting
- High body temperature
- High body temperature
- Pain does not go away when you take painkillers
- Cheek or jaw swollen
What is the best painkiller for toothache?
- Teeth infections are normally inflammatory based infections. Generally, over the counter non-steroidal anti-inflammatory medication are all that you will need. Everyone reacts differently to painkillers for dental pain. There are a few over the counter painkillers which are readily available.
- Ibuprofen- this can really help with toothache as it is an anti-inflammatory as well as an analgesic. It is not advised for asthmatics or people with certain stomach problems
- Paracetamol- This is readily available over the counter and comes in tablet and soluble. Many patients find this effective for dental pain.
- Paracetamol and Codeine or Paramol- is combination tablet. The codeine component is an opioid and can cause drowsiness which may impair normal function. It is advised to seek an urgent dental care if you have toothache.
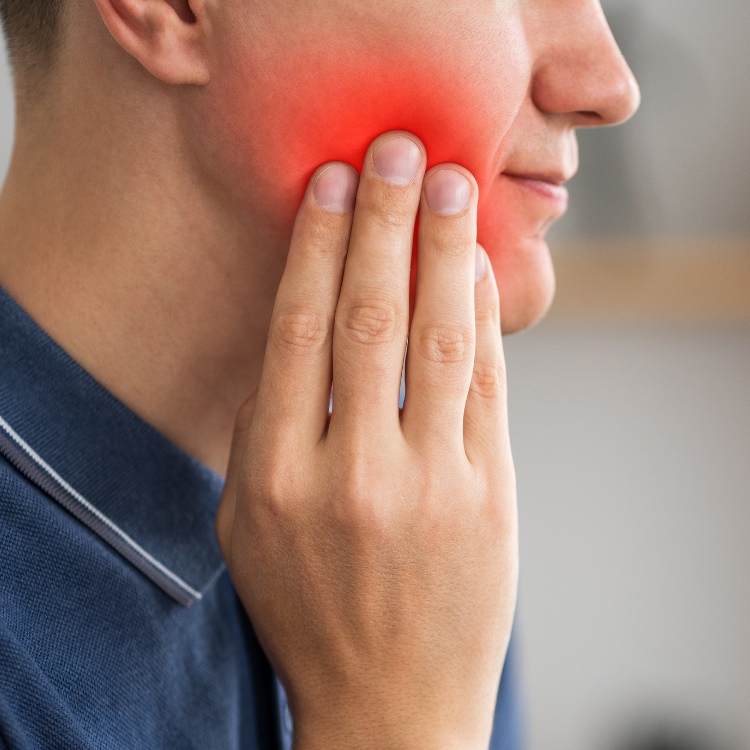
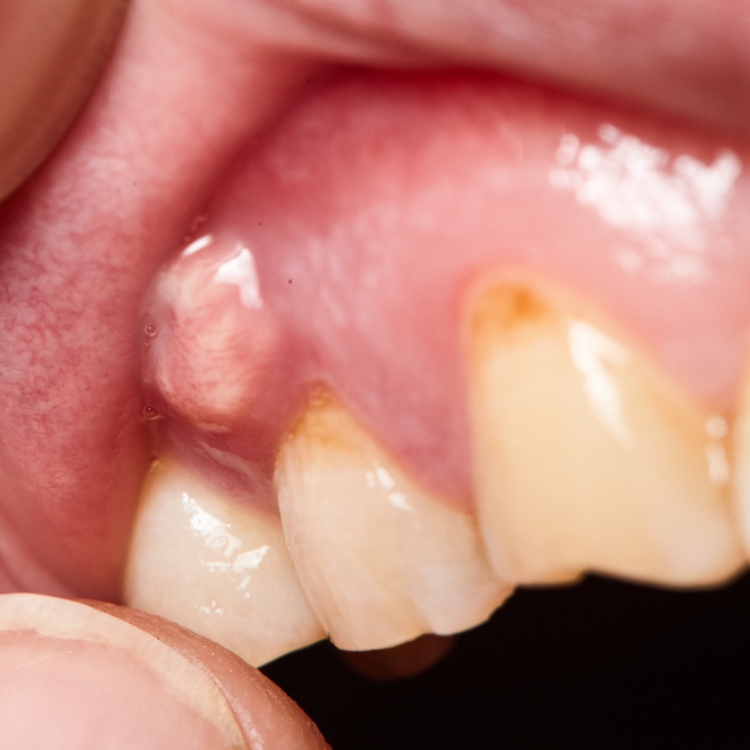
What are the symptoms of a dental abscess?
Symptoms of an abscess in your tooth or gum may include:
- An intense, throbbing pain in the affected tooth or gum that may come on suddenly and gets gradually worse
- Pain that spread to your ear, jaw and neck on the same side as the affected tooth or gum
- Pain that spread to your ear, jaw and neck on the same side as the affected tooth or gum
- Pain that’s worse when lying down, which may disturb your sleep
- A tender, discoloured and/or loose tooth
- Bad breath and/or an unpleasant taste in your mouth
If the infection spreads, you may also develop a high temperature (fever) and feel generally unwell. In severe cases, you may find it hard to fully open breathing. your mouth and have difficulty swallowing or breathing.
What causes dental abscesses?
Your mouth is full of bacteria, which form a sticky film on your teeth called plaque. If you do not keep your teeth clean, acids produced by the bacteria in plaque can damage your teeth and gums, leading to tooth decay or gum disease.
The following can increase your chances of developing a dental abscess:
- Poor oral hygiene – plaque can build-up on your teeth if you don’t floss and brush your teeth regularly
- Consuming lots of sugary or starchy food and drink – these can encourage the growth of bacteria in plaque and may lead to decay that can result in an abscess
- Having a weakened immune system – this includes people with certain underlying health conditions, such as diabetes, and those having treatment, including steroid medication or chemotherapy


What are the treatment options for a dental abscess?
- Removing the Affected Tooth (Extraction) – this may be necessary if root canal treatment is not possible
- Root Canal Treatment – a procedure to remove the abscess from the root of an affected tooth before filling and sealing it
- Incision and Drainage – where a small cut (incision) is made in the gum to drain the abscess (this is usually only a temporary solution and further treatment may be needed
Local anaesthetic will usually be used to numb your mouth for these procedures. More extensive operations may be carried out under general anaesthetic (where you’re asleep). Antibiotics aren’t routinely prescribed for dental abscesses, but may be used if the infection spreads or is particularly severe.
